Scalable metal-organic framework electrodes boost efficiency and cut costs for hydrogen production
A research team led by Prof. Zhao Shenlong from the National Center for Nanoscience and Technology (NCNST) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed scalable metal-organic framework (MOF) electrodes for alkaline water electrolysis, featuring facile synthesis, high efficiency, and industrial compatibility.
As the global energy transition accelerates, hydrogen has emerged as a clean and versatile energy carrier capable of decarbonizing high-emission industries and transportation sectors.
Renewable electricity-driven water splitting offers a sustainable route to green hydrogen production; however, its applications have been hindered by the scarcity of efficient, scalable, and durable electrodes for the kinetically sluggish oxygen evolution reaction (OER).
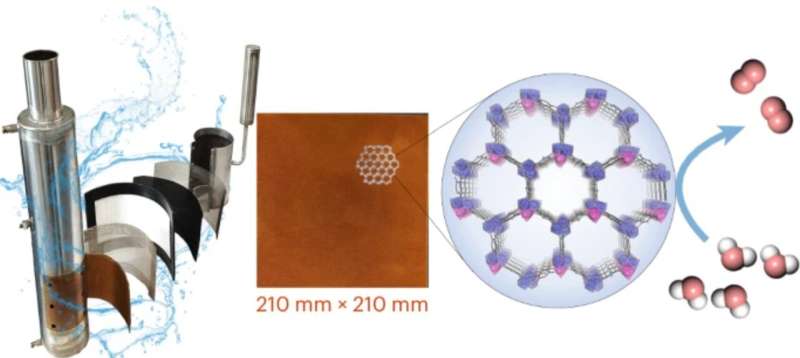
Using ultrasonication, researchers produced kilogram-scale quantities of MOF powders, and via room-temperature electrodeposition, they fabricated large-area electrodes. When integrated into alkaline electrolysis systems, these electrodes demonstrated low energy consumption of 4.11 kWh Nm−3 H2 and stable operation for more than 5,000 hours.
The excellent performance of the MOF electrodes arises from cerium (Ce) doping which tunes the electronic structure of cobalt (Co) active sites, substantially boosting OER kinetics. In addition, the lattice distortion and high surface area of the bimetallic CoCe-MOF enhance the mass transport (water/gas diffusion) and electrolyte accessibility, improving catalytic efficiency in practical devices.
The electrodes enabled efficient hydrogen production at a cost of just US$2.71 per kilogram because of their structure, which lowers the cost, underscoring their strong potential for sustainable large-scale applications. The research is published in the journal Nature Chemical Engineering.
This study offers a commercially viable way for MOF-based electrolysis technologies to reshape the energy landscape. Further effort should be made to optimize the synthesis process to ensure consistent performance during large-scale production and to expand the compatibility with different industrial electrolysis systems.
More information:
Yingjie Guo et al, Scalable metal–organic framework-based electrodes for efficient alkaline water electrolysis, Nature Chemical Engineering (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s44286-025-00262-2
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Citation:
Scalable metal-organic framework electrodes boost efficiency and cut costs for hydrogen production (2025, August 25)
retrieved 26 August 2025
from https://techxplore.com/news/2025-08-scalable-metal-framework-electrodes-boost.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
Comments are closed