Pet technology, meant to provide help and security for pets and owners, has vulnerabilities of its own
Pet owners are increasingly turning to technology for various pet care purposes such as feeding, health monitoring and activity and movement tracking. Much of this technology operates via devices and apps connected to the Internet of Things (IoT), thereby presenting privacy and security risks to those who use them.
What are the risks, how serious are they, and what measures have pet owners taken to protect themselves?
These issues and questions are the topic of a new study titled “Security and privacy of pet technologies: actual risks vs. user perception” by a research team from the U.K.’s Newcastle University and the University of London. It is published in Frontiers in the Internet of Things.
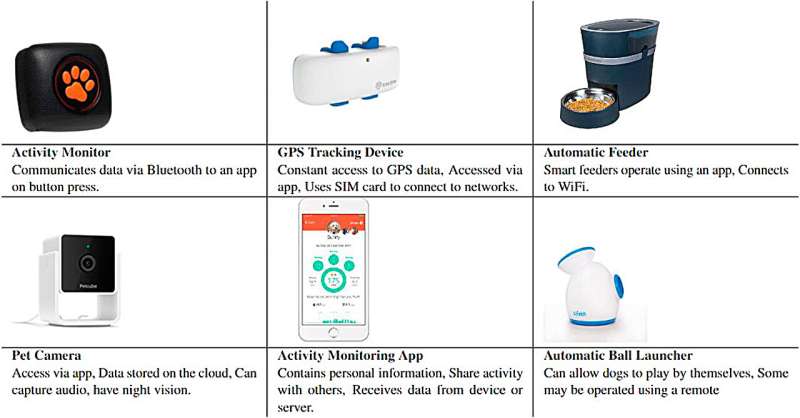
Technologies are available for many aspects of pet care. Owners can use apps and devices to remotely feed their animals; dispense them water and medication; play with them (e.g. automatic ball launchers for dogs); directly watch and listen to them via cameras; and via wearables, monitor their activity and track their movements via GPS.

However, despite pet tech’s projected market value of $3.7 billion by 2026, only a few studies to date have specifically addressed its privacy and security. That it functions via the IoT implies that in the event of a security breach, an owner’s personal information—such as their home address and details on household residents, including pets and children—could be exposed; or that an app or device tasked with a crucial function—such as a medication dispenser—could be misused or simply shut down.
In this new investigation, the researchers first analyzed the privacy and security practices and vulnerabilities of 20 commonly-used pet tech apps, and then surveyed a group of 593 users from Germany, the UK and the US to ascertain which technology they were using; their experiences with its security vulnerabilities; their awareness, needs, and concerns over such; and the measures they had taken to protect themselves and their pets.
The researchers also performed a detailed assessment of legislation from seven European nations, the European Union, and the U.S. state of California addressing animal welfare and privacy for specific mentions of pet technology with regard to privacy and security. Finally, the team compared the users’ perceptions of and concerns about the technology to its actual risks.
A lack of regulation and loose technology security
Among the notable findings, the assessment found that in contrast to laws regulating the use of tech to collect and store human-related data, almost no legal regulation exists to set privacy and security standards in the area of pet technology. The team confirmed this through discussion with animal technology experts in both academia and industry.
The implications of this gap are profound. The paper states, “Given the lack of regulation, animal applications that do not store any data relating to people do not need to follow the same restrictions as apps designed for humans. However, many of these apps do capture data about people or data relating to the actions of individuals.”
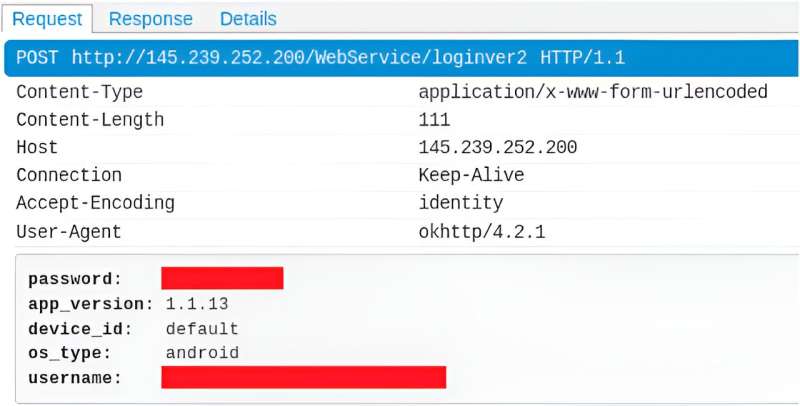
In fact, the team found that two of the 20 apps they looked at “had the user’s login details visible in plain text within non-secure HTTP traffic,” according to the paper. They also found that one of these apps would permit a bad actor to determine the exact location of a user’s pet, and that both provided a wealth of detailed information about users (name, address, phone number, email) and their pets (health conditions, medications, and more).
The researchers contacted the companies behind both apps regarding these vulnerabilities. One company subsequently implemented HTTPS encryption for its communications; the other never responded.
More information:
Scott Harper et al, Security and privacy of pet technologies: actual risks vs user perception, Frontiers in the Internet of Things (2023). DOI: 10.3389/friot.2023.1281464
© 2024 Science X Network
Citation:
Pet technology, meant to provide help and security for pets and owners, has vulnerabilities of its own (2024, January 26)
retrieved 27 January 2024
from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-01-pet-technology-meant-pets-owners.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
Comments are closed